Ocular diseases can damage the optic nerve. Irreversible vision loss occurs because of significant optic nerve damage or degeneration of the optic nerve. Prevention and treatment are the first steps to take because vision loss cannot be restored after optic nerve damage.
The Definition of the Optic Nerve
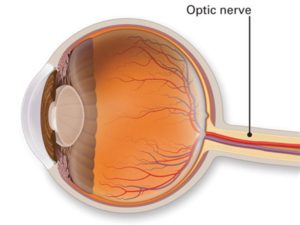
The optic nerve is part of the eye, and it is also known as the second cranial nerve, or simply CN II, and it is a continuation of the spine and brain’s central nervous system.
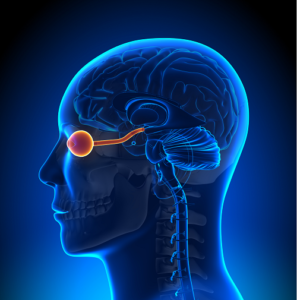 The optic nerve is critical to vision. Millions of nerve fibers make up the optic nerve which transmits visual information from the retina to the vision centers of the brain. The brain then interprets this sensory data so you can see. In short, the optic nerve is responsible for transferring visual signals to the brain.
The optic nerve is critical to vision. Millions of nerve fibers make up the optic nerve which transmits visual information from the retina to the vision centers of the brain. The brain then interprets this sensory data so you can see. In short, the optic nerve is responsible for transferring visual signals to the brain.
Symptoms of Optic Nerve Damage
The symptoms of optic nerve damage can either be temporary or permanent depending on the condition. Common signs include:
- Color blindness (loss of color vision). Some cases of color blindness are caused by genetic factors, but there are also non-genetic reasons such as injury to the eye, or the part of the brain that perceives color.
- One side vision loss is caused by nerve damage that only affects one eye.
- Peripheral vision loss in both eyes is caused by injury to the area behind the eyes where the optic nerves meet (optic chiasm).
- Visual field loss in one side of both eyes is caused by damage to the pathway that connects the optic chiasm to the part of the brain that registers visual information.
- Night blindness is caused by one of several conditions including glaucoma, cataracts, retinitis pigmentosa, etc.
Our suggestion is to contact your health care provider or eye doctor if you experience severe eye pain, chronic headaches, vision changes, or vision loss. Early diagnosis can help manage the condition or prevent future vision loss.
Common Optic Nerve Damage Causes
Visual problems, including vision loss or legal blindness, can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, changes in blood flow, clogged vessels, disease, exposure to harmful elements, etc.
Common risk factors for nerve damage include:
-
- Age, especially those over 50 years
- High cholesterol levels
- Sleep apnea (sleep-related breathing disorder)
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Smoking cigarettes
- Narrow blood vessels
- Certain drugs such as sildenafil, isoniazid, linezolid, amiodarone, etc.
Besides, following health conditions also harm the optic nerve and have an impact on vision directly.
Trauma

Causes
Any serious lacerations or bleeding inside the eye will harm the optic nerve. Eye injuries can result from falls, automobile accidents, sports injuries, and being punched or kicked in the eye. Optic nerve damage caused by trauma is typified by a decline in vision or vision loss which usually occurs 3 to 6 weeks after the trauma occurred.
Prevention & Treatment
Our suggestion for trauma is to avoid putting your eyesight at risk. Visit an emergency department right away if you suffer from any eye injuries. Treat any eye injuries as potential emergencies, and never delay in contacting or seeing an eye doctor.
Glaucoma

Causes
Glaucoma is caused by too much pressure inside one or both eyes, and it is defined as a group of eye conditions that can damage your optic nerves.
Early signs of glaucoma are rarely evident. But once this pressure begins to harm the optic nerve, it can result in serious side (peripheral) vision issues that get worse over time as it progresses and eventually causes irreversible levels of blindness.
Prevention & Treatment
Glaucoma cannot be prevented. But there are things you can do to limit or eliminate potential vision loss.
Regular eye examinations are essential for prevention, especially for people whose vision appears normal. This is because individuals with glaucoma or ocular hypertension often experience no symptoms until they are examined, the only way to diagnose glaucoma is with a comprehensive dilated eye exam.
Some physical activities and exercise can occasionally relieve ocular pressure, but some activities can increase it. A doctor can advise you on the best exercises to do.
Optic Neuritis
Causes
Optic neuritis is characterized by damage causing optic nerve swelling. To be specific, the optic nerve and the protective covering that surrounds it are often damaged by inflammation that frequently develops in the portion of the optic nerve that comes before the optic chiasm.
 Optic neuritis typically occurs in adults younger than 45, more frequently in females than males. Affected eyesight related to nerve damage in multiple sclerosis can lead to loss of mobility and sensory functions, along with other debilitating conditions.
Optic neuritis typically occurs in adults younger than 45, more frequently in females than males. Affected eyesight related to nerve damage in multiple sclerosis can lead to loss of mobility and sensory functions, along with other debilitating conditions.
Prevention & Treatment
Most people with optic neuritis could recover without treatment, but medications may be necessary to speed up recovery and prevent vision loss.
Intravenous steroid therapy is used to treat optic neuritis too and lessen inflammation. Additionally, if the cause of the optic neuritis is known, the underlying condition can be treated.
Optic Nerve Colobomas
Causes
Coloboma is a condition in which the tissues in and around the eye are absent, which is most likely caused by genetic defects or chromosomal abnormalities. The condition can be inherited or happen spontaneously and can affect one or both eyes.
Prevention & Treatment
Usually, people who only have one eye affected by coloboma may need to use specific eye drops or wear an eye patch to prevent amblyopia. People with iris colobomas can have surgery to make their pupils appear more rounded. But for another type of colobomas, surgery cannot replace the part of the eye that’s missing. Some approaches can assist coloboma patients to make the most of their vision.
-
-
- Contact lenses or eyeglasses. People with coloboma who have refractive problems could wear eyeglasses or contact lenses to see more clearly. Additionally, colored contact lenses can be used by those with iris colobomas to enlarge their pupils.

- Electronic video magnifiers. Compared with optical glasses, electronic low vision aids allow users to view things in a variety of sizes or typefaces, and system color schemes allow people who are color blind to see easier.
-
Optic Nerve Drusen
Causes
Optic nerve drusen are caused by an atypical buildup of protein and calcium in the optic nerve. The yellowish deposits are frequently found in both eyes and are unusual, but they typically do not impair vision. Only in a few cases; patients may experience loss of peripheral (side) vision or temporary flickering or grey of vision.
Prevention & Treatment
There is no surgical option to treat optic nerve drusen. People with optic nerve drusen usually only learn about it during a comprehensive eye exam performed by their eye doctor. Fortunately, most patients who have optic nerve drusen will not experience any vision problems.
Protect Optic Nerves
It is possible to avoid the risk of ocular nerve injury. You can safeguard your eyesight and optic nerve by taking the following precautions:
- Get regular eye exams. Regular eye exams can assist in identifying disorders that affect the eyes before they harm the optic nerve. For instance, glaucoma can be treated or prevented early on and lowering the risk of vision loss. Similarly, the risk of visual impairment and blindness of diabetic retinopathy can be substantially reduced by early detection with effective treatments.
- Stop smoking. Smoking reduces blood flow throughout the body, which may cause optic nerve damage, and increases the risk of glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and other eye diseases. Wear eye protection (such as sunglasses, goggles, low vision aids, etc.) when engaged in sports or activities.

- People with eye problems are at greater risk for eye damage from the sun’s rays. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, UV 400-protected sunglasses can block 99% to 100% UVA and UVB. Using blue-light filters when watching media devices can also slow down retinal deterioration and lower the risk of developing color blindness.
- Low vision aids such as electronic magnifiers can also help visually impaired or partially colorblind people to manage well daily tasks such as travel activities, self-care issues, and reading-related tasks well.
- Maintain physical fitness by engaging in exercise and eating a nutritious diet. Diabetes and high blood pressure are two risk factors that affect vision and nerves. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help people keep blood sugar and weight at a healthy level and stay away from illnesses like diabetes and high blood pressure.
Prevention Is the Primary Method of Treating Optic Nerve Damage
Optic nerve damage treatments may not be able to restore lost vision in the short term. Most of the time, early discovery and effective treatment are the best ways to prevent future harm and stop symptoms from worsening. Please keep in mind that you ought to seek an ophthalmologist’s guidance for proper health instructions if you have eye problems, feel uncomfortable, or are experiencing eye pain.
See more:
Optic nerve: Anatomy, function and conditions
Causes and symptoms of optic atrophy
Reference
Ayaga, V. (2022, June 14). Optic Nerve – Function, Anatomy & Associated Conditions. Vision Center. Retrieved August 2, 2022, from https://www.visioncenter.org/eye-anatomy/optic-nerve/
Ayaga, V. (2022b, August 2). Optic Neuropathy – Symptoms, Causes & Treatment. Vision Center. Retrieved August 3, 2022, from https://www.visioncenter.org/conditions/optic-neuropathy/
What Is Your Optic Nerve? (2022, July 1). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved August 2, 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22261-optic-nerve


