Retinal detachment disrupts the retina’s normal function, leading to low vision and sometimes causing blindness [1]. The appropriate recommendation would be to undergo retinal detachment surgery. Retinal detachment surgery has a high success rate in restoring an individual’s vision and helps prevent further retina detachment [2]. This article will discuss various retinal detachment surgeries, how to prevent retinal detachments in daily life, and how low vision aids help with retinal detachment prevention and post-retinal detachment surgery recovery. First, let us see what’s retinal detachment and the signs of retinal detachment.
What are Retina and Retinal Detachment?
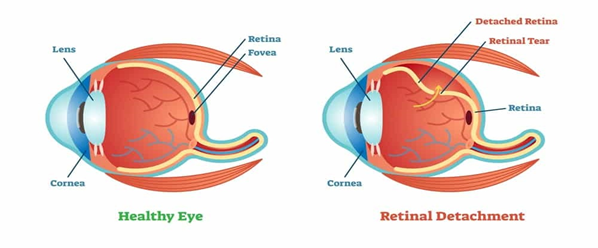
A retina describes the thin layer of tissue found near the optic nerve at the back of the human eye. The retina’s primary purpose is to receive light and convert it to neural signals. The retina sends these signals to the human brain for visual recognition [3]. Pigment epithelial detachment means that the thin retina tissue is pulled away from the different layers of the eye tissues (see figure 1 above). When retinal detachment happens, the retina pulls away from the supporting tissues causing reduced vision and, when not treated, may cause blindness.
Prevalence of Retinal Detachment
Incidences of retinal detachment are very rare in individuals, with studies showing that it affects 1 to 17 individuals out of every 10000 [6]. The study also shows that males are highly susceptible to the condition than females. In addition, the condition is particularly common in South East Asia and most European countries [6].
What are the Symptoms of Retinal Detachment?

According to Mayo Clinic, the following are the symptoms of retinal detachment [5]
- The eye appears to have many floaters, tiny specs drifting away from the peripheral view/field of vision.
- The patient experiences flashes of light in the affected eye
- The patient’s vision becomes blurred
- Overtime there is a gradual deterioration of peripheral vision evident in a grey curtain
- A curtain-like shadow blocks the eye’s vision on the peripheral field.

Causes for Retinal Detachment
The three primary retinal detachment types are rhegmatogenous, tractional and exudative detachments which have different causes depending on the type. The rhegmatogenous retinal detachment describes a condition arising from retina dialysis, retinal break or retinal hole forming within the tissues that make up the retina [7]. When this happens, the detached vitreous enters the space beneath the neurosensory retina leading the retina detachment, retinal injury or inflammation. The common cause for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is ageing, as the vitreous changes its composition in old age[8].
In addition, tractional retinal detachment describes the proliferation of the membranes that make up the vitreous retinal surface pulling the retina from the neurosensory retina. When the force pulling the retina is high enough, it can separate the neurosensory nerve from the attached retina [9]. The most common cause of tractional retinal detachment is diabetes and prolonged high blood pressure.
Lastly, exudative retinal detachment describes a condition where fluids fill subretinal space, pushing it away and may lead to a buildup of fluids inside the blood vessels and even swelling of the eye. This results in eye inflammation [7]. The primary causes for exudative detachments include inflammatory infectious and neoplastic conditions with the choroid or the retina.This post is sponsored by our partners Wigs
Risks for Retinal Detachment
The following are the primary risk factors for retinal detachments [5]
-
- Patients older than 50 years
- The patient has a medical history of a previous diagnosis of retinal detachment
- The medical history indicates a previous history of retinal detachment
- Medical diagnosis indicates extreme myopia or shortsightedness
- The patient underwent previous medical surgery
- The patient has a severe eye injury
Diagnosis for Retinal Detachment
The doctor may diagnose a retinal detachment through either retinal detachment examination or retinal detachment ultrasound [10]. In the retinal examination, the doctor uses high light to illuminate the back of the eye, including the retina, to get a detailed view of the retina, areas where detachments occurred and the presence of inflammation or retinal joles [10]. On the other hand, in retinal detachment ultrasound, the doctor is interested in investigating the presence of vitreous fluids [10]. Patients are therefore recommended to visit their eye doctors regularly when they start experiencing retinal detachment symptoms.
How retinal detachment causes blindness?
 A retinal detachment condition may lead to permanent blindness when the condition is not treated or prevented in time [11]. Patients with symptoms of retinal detachment are advised to visit a doctor immediately, reducing the risks of permanent blindness. This means that the condition should be treated as an emergency and should be treated in a matter of days through recommended preventative measures such as retinal detachment surgery [11].
A retinal detachment condition may lead to permanent blindness when the condition is not treated or prevented in time [11]. Patients with symptoms of retinal detachment are advised to visit a doctor immediately, reducing the risks of permanent blindness. This means that the condition should be treated as an emergency and should be treated in a matter of days through recommended preventative measures such as retinal detachment surgery [11].
What Treatment Options Are Available for Retinal Detachment?
There are many treatment options available for patients experiencing the condition of retina detachment, the most successful intervention is retina detachment surgery which the eye doctor recommends depending on the extent of the detachment and the type of retinal detachment the patient has [12]. Three types of retina detachment surgery are categorized into pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckle and vitrectomy. There are incidences where a patient may be expected to undergo a treatment intervention in more than one surgery type or a repeated surgery of a similar type of surgery.
Different types of Retinal Detachment Surgery
Torn retina surgery
The doctor recommends laser surgery or a freeze treatment when the patient’s retina has pears, holes or a tear due to aging, prevalent diseases, and sometimes eye injury.
Laser treatment (photocoagulation)
With laser treatment or photocoagulation surgery, the doctor illuminates a light beam to the back of the eye that burns around the tear or hole in the retina. This burn creates small scars and tears, which help fix the tear on the patient’s retina and help the retina regain its primary position. Post retinal detachment treatments are special eye drops that prevent the eye from swelling [13].
Freezing treatment (cryopexy)
The other method that eye doctors help patients with torn retinas is freeze treatment, also known as cryopexy. In this treatment option, the eye doctor uses freezing probes to freeze the torn tissue and make scars around the tear from the thin retina [13]. This tear around the sclera helps to pull back the retina and keep it in place. Post retinal detachment treatments include the eye drops the doctor gives to help prevent swelling. Patients are also advised to avoid engaging in activities such as lifting to help the eye heal faster.
Detached retina surgery
Pneumatic retinopexy
In this type of intervention, the eye doctor injects a small air bubble into the patient’s eye, which helps to push the retina back to its original position, where the patient may now undergo secondary treatments of photocoagulation and cyopexy [14]. The patient can see the air bubble after the doctor performs the procedure, but it disappears with time. Post retinal detachment care includes holding the head in a specific position to keep the air in the right spot and avoiding heavy activities [15].
Scleral buckle
When the patient undergoes the scleral buckle surgery, the doctor places a tiny flexible band on the sclera part of the eye, which helps to push the retina into position, reattaching it into the appropriate position. Jon Hopkins Medicine research shows the downside of this intervention is that the band remains inside the eye after the procedure [16]. In post-retinal detachment surgery, the patient is also expected to undergo photocoagulation and cyopexy interventions to repair the tears in the retina.
Vitrectomy
This surgery treats various problems associated with retina detachment and vitreous fluids. When performing the procedure, the eye doctor removes the vitreous fluids and replaces them with other solutions [17]. The patient then undergoes photocoagulation and cyopexy interventions, which help restore the tear around the retina. Risks involved with this intervention include infection, bleeding, eye development, high pressure, and other problems which require the patient to regularly visit the hospital and remain under hospital care until they heal [17].
Low Vision Aids for Prevention and Post-Retinal Detachment Surgery
Retinal detachment is usually caused by aging, so is frequently unavoidable. But wearing safety goggles or other protective eyewear when engaging in outdoor activities, such as playing sports, mountain climbing, cycling, etc., can reduce the risk of developing retinal detachment from an eye injury. Wearable E-glasses visual aids Acesight/ Acesight S, with a high level of security, is perfect eyewear for individuals who want to participate in more practice activities and offer sufficient protection for the visually impaired. More Tips About How to Choose Safety Eyewear

On the other hand, although retinal detachment surgery contributes to vision restoration, it happens that eyesight may not fully recover. In this case, low vision aids are used to protect the remaining vision contact lenses, which may result in more severe damage), and make it easier for visually impaired people to read and see things. Common used low vision aids include handheld electronic video magnifiers, desktop electronic video magnifiers, VR or AR E-glasses, etc. Among them, E-glasses, such as IrisVison, Acesight VR, and Acesight S, is the most well-liked visual aids for retinal detachment.
Living Normal with Retinal Detachment/Low Vision
 Although the condition may cause an individual to become visually impaired and sometimes permanent blindness when not attended to immediately, depending on the degree of vision loss, the individual’s lifestyle will change as they are now dependent on low vision aids [10]. The patients are expected to get glasses which have safety lenses and magnifiers. In addition, their homes will need proper lighting for reading and engaging in other activities [10]. These individuals will also need help from technologies such as the Zoomax series, digital talking books and even motion-activated lights [10]. Nevertheless, with increased online networking, visually impaired patients can talk to others with the condition to access support groups and resources for people living with impaired vision [10].
Although the condition may cause an individual to become visually impaired and sometimes permanent blindness when not attended to immediately, depending on the degree of vision loss, the individual’s lifestyle will change as they are now dependent on low vision aids [10]. The patients are expected to get glasses which have safety lenses and magnifiers. In addition, their homes will need proper lighting for reading and engaging in other activities [10]. These individuals will also need help from technologies such as the Zoomax series, digital talking books and even motion-activated lights [10]. Nevertheless, with increased online networking, visually impaired patients can talk to others with the condition to access support groups and resources for people living with impaired vision [10].
Long-term Prognosis for Retinal Detachment
To sum up, pigment epithelial detachment may cause an individual to become visually impaired or permanently blind. Patients are advised to treat the condition as an emergency and seek medical interventions, and retinal detachment surgery. Nearly 90% of retinal detachments will be successfully fixed in a single operation. Retina re-detaches may happen, but approximately 95% of subsequent operations are ultimately successful and let patients return to full vision. However, your vision recovers also rely on the length, scope, and location of the detachment. If the macula, the portion of the retina responsible for central vision, has detached, it is doubtful that full vision would ever return, even if the procedure is successful. In these cases, we need low vision assistive technology, such as E-glasses, and low vision electronic video magnifiers, to maximize our limited vision. In addition, eye injuries happen when people participate in indoor or outdoor activities. We should wear safety eyewear while using power tools and participating in both indoor and outdoor activities to prevent eye injuries. Given how valuable vision is, we should be sure to practice healthy eye habits daily to protect our eyesight.
References
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/retinal-detachment
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/retinal-detachment
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinal-detachment/symptoms-causes/syc-20351344
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinal-detachment/symptoms-causes/syc-20351344
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551502/#:~:text=The%20incidence%20of%20rhegmatogenous%20retinal,getting%20a%20rhegmatogenous%20retinal%20detachment.
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/retinal-detachment/types-and-causes-retinal-detachment#:~:text=The%20most%20common%20causes%20of,%2Drelated%20macular%20degeneration%20(AMD)
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4709524/pdf/eye2015171a.pdf
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10705-retinal-detachment
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinal-detachment/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351348
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/retinal-detachment/symptoms-causes/syc-20351344#:~:text=Rhegmatogenous%20detachments%20are%20caused%20by,causing%20you%20to%20lose%20vision.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5859893/
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/retinal-detachment/laser-surgery-and-freeze-treatment-retinal-tears
- https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/retinal-detachment-surgery
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/pneumatic-retinopexy#:~:text=Pneumatic%20retinopexy%20is%20a%20procedure,visual%20information%20to%20your%20brain.
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/scleral-buckling#:~:text=Scleral%20buckling%20is%20a%20type,of%20your%20retina%20and%20eye.
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/vitrectomy#:~:text=What%20is%20vitrectomy%3F,middle%20portion%20of%20your%20eye


